The industrial revolution began with Industry 1.0, which utilised water or steam powered machinery, followed by Industry 2.0, which utilised assembly lines and electricity, and ultimately Industry 3.0, which utilised computers for production and workplace operations. Additional advancements resulted in Industry 4.0 (also known as IIoT), which employs electronic devices for even greater efficiency, performance and sustainable productivity. Through digital twins and intelligent network connections, the industrial revolution will play a significant role in the next level of industries. The patent filings in IIoT technology had an upsurge in the year 2018, due to acceleration in edge computing and edge intelligence.
IoT often emphasises consumer convenience, whereas IIoT concentrates on ROI to ensure that organisations get the most out of using IIoT. IoT applications link devices from several industry sectors, such as agriculture, healthcare, consumer goods, government, transportation, and urban areas. On the other hand, IIoT applications link equipment and gadgets in the manufacturing, oil and gas, and utility sectors to have access to new data-driven capabilities. In addition, compared to IoT applications, which are user-focused, IIoT applications are more focused on enhancing efficiency and increasing health or safety.
IIoT and its Need, Challenges, Technology Domain and Applications
Technology Domain
-
Telecommunications
-
Digital Communications
-
Computer Technology
-
Control-High degree of automation
-
Electrical Machinary, Apparatus, Energy
-
Medical Technology
-
Audio-Visual Technology
-
Chemical Engineering
Need of IIOT
-
Business and Industries may operate more effectivelly
-
The device that collect data can comunicate with other devices
-
Informed decision-making based on real business data
-
Obtain real-time data-process of Industrial organisation in order to improve
-
Know about clients and to improve processes and serve clients
-
Make Reactive Maintaineance Predictive and preventive
-
Remote updates, Monitoring, Control,
-
Enhance Production Quality
Challenges in IIOT
-
High Investment Cost
-
Secure Data Storage and Management
-
Connectivity Outages
-
Security - cyber attacks
-
Limited Interoperability - difficult to communicate and exchange data
-
Limited skilled workforce
-
High maintainance costs
-
Equipment downtime
-
Complicate management of the heterogeneous data streams
Applications
-
Industries
-
Factories
-
Smart Robotics
-
Smart Logistics
-
Software Integration
-
Power Management
-
Agriculture
-
Healthcare
-
Manufacturing Industry
-
Transportation
IIoT patent filing trend
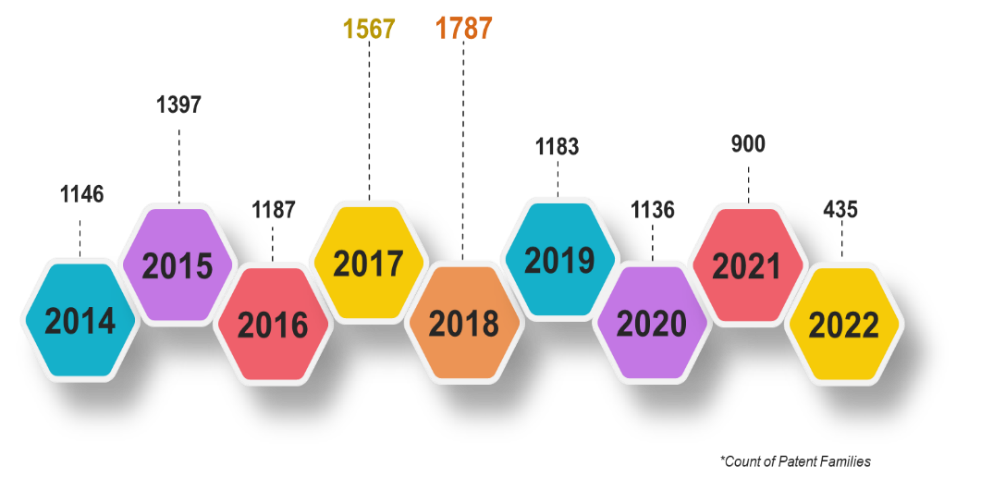
IIoT patent filing trend

Top Assignees in IIoT – Last 5 years







China is the leading country for patent filing in IIoT and its related technologies. The patent filing trend in China for IIoT shows Huawei, Samsung, Qualcomm, LG and Ericsson are the leading players who are actively filing patents. Most number of patent families (911) were filed in China in the year 2018. After China, maximum patents get filed in the United States in IIoT where companies such as Samsung, LG, Huawei, Ericsson, Apple are filing substantial amount of patents.
Future of IIoT
- Increase production – by connecting machines and devices to the internet, it is possible to gather and analyse data in real time to spot potential problems before disruptions
- Create new hybrid business models
- Exploit intelligent technologies – in order to foster innovation and revamp workforce
- Security strategy and architecture to minimize risk – the attacker is prevented from accessing the main devices directly and can easily trap them






