LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN, which stands for “Long Range Wide Area Network,” is a wireless communication protocol and technology designed for low-power, wide-area networks. LoRaWAN is specifically optimized for long-range communication with low data rates, making it suitable for applications that require remote monitoring, tracking, and control of devices and sensors over extended distances.
How LoRa is different from Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi has a small range and uses a lot of battery. LoRa was created specifically for IoT devices. LoRa allows for low-power transmissions over distances of more than 10 km in rural areas. LoRa is a 2012 patented wireless communication standard. In addition to LoRa, there are other low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) wireless options, such as NB IoT or LTE Cat M1. Numerous IoT devices are spread out over broad areas and have short battery lives. LoRa is especially suitable for these gadgets.
Key Features and Advantages
Long Range:
Enables connection across large regions, making it suitable for massive deployments.
Low Power:
Devices may run on battery power for a long time, which lowers maintenance requirements.
Scalability:
Allows for a high number of devices to be supported, allowing for the expansion of IoT applications.
Cost-Effective:
Offers a connectivity solution that is less expensive than alternatives like cellular networks.
Low Data Rates:
Low data rates are ideal for transmitting small amounts of data periodically.
Security:
Provides robust security features such as encryption and device authentication to safeguard data transmission and ensure device integrity.
Environmental Sustainability:
Contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing the need for frequent battery replacements and minimizing waste.
Deployment Flexibility:
It is deployed in various settings, including urban and rural areas, to cater to diverse connectivity requirements.
Why LoRaWAN:
- LoRaWAN is a versatile technology that enables effective data collection from distributed sensors in smart city applications such as smart lighting, waste management, parking, and environmental monitoring.
- LoRaWAN is utilized by farmers for precision agriculture, enabling them to monitor soil conditions, weather, and crop health, optimizing irrigation, fertilization, and pest control.
- LoRaWAN is used to link sensors and devices, monitor equipment health, track inventories, and assure effective operations in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and supply chain management.
- LoRaWAN is utilized in industries like manufacturing, logistics, and supply chain management to connect sensors and devices, monitor equipment health, track inventory, and ensure efficient operations.
- LoRaWAN is a technology utilized for home automation and smart home applications, offering extended coverage for devices in remote areas of a property.
How Does LoRaWAN Work?
End devices, gateways, network servers (NS), and application servers are the four components of a LoRaWAN network architecture. Because of the long-range characteristic of LoRa, the network architecture between gateways and end devices is star-shaped, and they can employ single-hop transmission between them. In the end devices portion, there are six typical applications listed, that end devices can broadcast to many gateways at the same time, while gateways forward LoRaWAN protocol data between NS and end devices.
Device Communication:
LoRaWAN networks are designed to facilitate communication between low-power IoT devices (also known as end devices or nodes) and gateways.
End devices can include sensors, meters, and other IoT devices that need to send data to a central system.
Long-Range Transmission:
LoRaWAN operates in the sub-GHz ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) bands, which vary by region (e.g., 868 MHz in Europe, 915 MHz in North America). This lower frequency allows signals to travel long distances and penetrate obstacles, making it suitable for wide-area communication.
Devices can transmit data over several kilometers, depending on the terrain and environmental conditions.
Low Power Consumption:
One of LoRaWAN’s key advantages is its low power consumption. End devices can operate on small batteries for extended periods, ranging from months to years, depending on the application and usage.
This is achieved through the use of low-power transceivers that minimize energy consumption during transmission and reception.
Data Rate and Adaptive Data Rate:
LoRaWAN supports various data rates, allowing devices to adjust their transmission speed based on the signal strength and distance to the gateway.
Adaptive Data Rate (ADR) is a feature that automatically optimizes the data rate for each device to maximize efficiency and conserve energy.
Communication Classes:
LoRaWAN defines three communication classes to suit different IoT application needs:
Class A: Bi-directional communication with the lowest power consumption. Devices are usually asleep and wake up periodically to send or receive data.
Class B: Adds scheduled receive windows for devices to listen for downlink data at specific times.
Class C: Allows continuous listening for downlink data, sacrificing some power efficiency for faster response times.
Current Trends and Future Outlook
Leading players in LoRaWAN market are Orange, KPN, SK Telecom, Cisco Systems, Everynet and Microchip Technology. The market size of Global LoRaWAN is expected to grow more than 40% CAGR through 2032.
Long Range Wide Area Network, is expected to experience significant growth in the coming years, offering a promising future for IoT connectivity across various industries. Its low-power, long-range capabilities will be crucial for smart cities, agriculture, healthcare, and other sectors. Its scalability will enable asset tracking and predictive maintenance, while its security features will protect critical infrastructure and data. Private networks will become more prevalent for organizations seeking control and reliability. Integration with 5G networks will enable seamless connectivity and low-latency IoT solutions.
Filing Trend of LoRaWAN (Patent Families over the years)
No Data Found
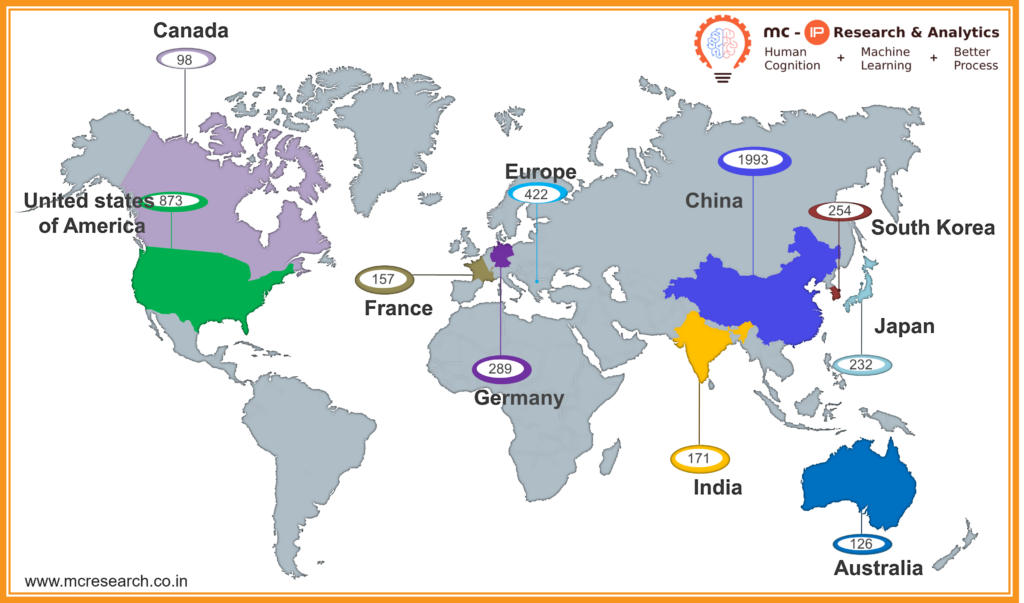
Geographical Distribution – LoRaWAN – Last 5 years
Top Players - Patent Families across Last 5 years
No Data Found
Why MCRPL?
MCRPL’s innovative integration of AI and human expertise (MCRANK) offers a distinct edge in the field of patent searches. This synergistic approach not only ensures efficiency and accuracy but also taps into the nuanced understanding that human experts bring to the table. By harnessing the power of cutting-edge AI tools alongside seasoned professionals, MCRPL delivers comprehensive, precise, and timely results for its clients. This unique blend of technology and expertise is assured to revolutionize the patent search process, making MCRPL a trusted partner for businesses and innovators seeking to safeguard their intellectual property and drive forward in an increasingly competitive market.
With plenty of experience of working on telecom standards and specifically on LoRaWAN, MCRPL can bring out actionable intelligence and can also forecast the roadmap for telecom industry in the coming future. MCRPL has the right talent and expertise on the subject matter as well as on technical knowhow to quench your thirst in the R&D space.
© Molecular Connections Private Limited
For more information, contact priorart@molecularconnections.com
For more updates subscribe IP Tech Insider
Also, you can place an order for your search on our online portal: https://ipsolutionshub.com/